Raising baby rabbits is a rewarding experience, but ensuring their proper nutrition is paramount for their healthy development. This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on every aspect of feeding baby rabbits, from the initial stages of nourishment to recognizing and addressing potential issues. It emphasizes the importance of appropriate feeding techniques, schedules, and supplemental care, ensuring optimal growth and well-being.
Understanding the specific nutritional needs of newborn rabbits is crucial. Their digestive systems are still developing, requiring specialized care and a gradual transition to solid foods. This guide offers a detailed overview of essential food sources, including milk replacers, and explores how to prepare and administer them safely. We will cover everything from sterilizing equipment to storing food properly, ensuring hygiene throughout the process.
Introduction to Baby Rabbit Feeding
The first few weeks of a baby rabbit’s life are critical for their survival and future development. Proper nutrition during this period is paramount, directly impacting their growth rate, immune system strength, and overall health. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail in feeding practices, ensuring optimal nourishment to support their growth and development.Appropriate nutrition during this delicate phase lays the foundation for a healthy and productive rabbit.
A carefully planned feeding regimen, tailored to the specific needs of young rabbits, is crucial for their well-being. This includes understanding the transition from mother’s milk to solid foods and maintaining a consistent feeding schedule.
Initial Stages of Feeding
The initial stages of feeding focus on providing the necessary nourishment for the baby rabbits, typically known as kits. Their digestive systems are still developing, and introducing solid foods too early can lead to digestive issues. The mother rabbit plays a crucial role in this transition, providing essential colostrum, the first milk, rich in antibodies that bolster their immune systems.
The kits should remain with the mother for at least 2-3 weeks to benefit from her milk and care.
Transition to Solid Food
As the kits’ digestive systems mature, a gradual transition to solid food is essential. This should be implemented around 3-4 weeks of age. Introducing too much or too little solid food can negatively impact their health and growth. The gradual transition involves providing a mix of soft, easily digestible foods, avoiding harsh or difficult-to-digest substances.
Feeding Schedule for the First Few Weeks
Understanding the feeding schedule is critical for ensuring consistent nourishment during the early weeks. The schedule needs to adapt to the kits’ growing needs. The following table provides a general guideline for the first few weeks of a baby rabbit’s life.
| Week | Food Type | Feeding Frequency | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 | Mother’s milk (Colostrum) | As needed | Sufficient to meet the kit’s needs |
| 3-4 | Soft pellets, finely chopped vegetables (like carrots, leafy greens, or sweet potato), and hay | 2-3 times daily | Small portions, easily digestible |
| 4-6 | Regular rabbit pellets, leafy greens, hay | 3-4 times daily | Increased portions as they grow |
Essential Food Sources for Baby Rabbits

Providing newborn rabbits with the correct nutrition is crucial for their survival and healthy development. Their digestive systems are still immature, making them highly susceptible to nutritional deficiencies. Properly formulated diets, including essential nutrients and appropriate feeding methods, are paramount for a successful outcome.The primary dietary needs of newborn rabbits, particularly in the first few weeks, revolve around the provision of adequate nutrition to support their growth and development.
This is primarily achieved through milk replacers and gradually introducing solid foods. The transition from milk to solid foods must be managed carefully to avoid digestive upsets.
Essential Food Sources for Newborn Rabbits
A newborn rabbit’s primary food source during the first few weeks is milk replacer. Solid foods are gradually introduced as their digestive systems mature. A variety of essential nutrients are crucial for proper development.
- Milk Replacer: This is the most vital source of nutrition for newborn rabbits. It provides crucial antibodies, proteins, and fats essential for immune function and growth.
- Enriched Formula: A well-balanced formula supplemented with essential vitamins and minerals supports the growth and development of the rabbit’s immune system. This ensures a comprehensive nutritional profile for the young rabbits.
Nutritional Composition of Food Sources
The nutritional content of milk replacers varies depending on the specific brand and formula. However, a good quality replacer should contain a balanced proportion of protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals crucial for healthy growth.
- Protein: Essential for building and repairing tissues, crucial for muscle development and overall growth. A suitable percentage is vital for appropriate development.
- Fat: Provides energy for growth and development. A balanced fat content supports metabolic processes and overall health.
- Carbohydrates: Supply energy for daily activities and support optimal growth. A suitable amount is essential for energy and development.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Essential for various bodily functions and immune development. A balanced ratio of vitamins and minerals is necessary for robust development.
Milk Replacer Types and Comparison
Different milk replacers cater to various needs and budgets. Careful selection is critical for ensuring proper nutrition.
- Commercial Milk Replacers: These formulas are commercially produced and formulated to meet the nutritional needs of newborn rabbits. They often include pre-measured ingredients, ensuring accurate and consistent nutrition.
- Homemade Milk Replacers: While possible, creating a homemade formula requires significant expertise in pet nutrition. A potential risk involves inaccurate nutrient proportions, potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies or imbalances.
Preparing and Administering Milk Replacer
Proper preparation and administration of milk replacer are crucial for successful feeding. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions meticulously.
- Preparation: Always mix the milk replacer according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Use lukewarm water and avoid extreme temperatures. This ensures the right consistency for absorption.
- Administration: Use a small, clean feeding bottle or syringe to administer the milk replacer. Ensure the feeding bottle is clean and sanitized. Proper feeding techniques are vital to prevent choking or aspiration.
Transitioning from Milk Replacer to Solid Food
The transition from milk replacer to solid food should be gradual. This helps prevent digestive issues.
- Introduction: Begin by introducing small amounts of rabbit-specific pellets and hay. Gradually increase the quantity of solid food while decreasing the milk replacer intake. This approach allows for a smooth transition.
- Monitoring: Closely monitor the baby rabbits for any signs of digestive distress, such as diarrhea or vomiting. Observe for any changes in their eating habits.
Milk Replacer Brand Comparison
| Brand | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | High protein content, readily available | Fast growth, good value | Potential for digestive issues in some rabbits |
| Brand B | Balanced formula, includes prebiotics | Improved gut health, potentially reduced digestive problems | Slightly higher cost |
| Brand C | Specialized formula for premature or weak rabbits | Enhanced support for vulnerable kits | Limited availability |
Preparing the Food for Baby Rabbits
Proper food preparation is crucial for the health and well-being of baby rabbits. A clean, sterile environment, and appropriate temperatures for food and water are essential to prevent illness and promote healthy growth. This section will detail the steps involved in ensuring that baby rabbits receive the best possible nutrition in a safe and hygienic manner.
Hygiene in Food Preparation
Maintaining meticulous hygiene is paramount when preparing food for baby rabbits. Contamination with bacteria or other pathogens can lead to serious health issues, even death. All surfaces, utensils, and equipment used in the feeding process should be thoroughly cleaned and sanitized to eliminate any potential sources of contamination. This includes using hot, soapy water to clean all surfaces and then disinfecting with a suitable sanitizer specifically designed for use around food.
Temperature Requirements for Food and Water
The temperature of food and water plays a significant role in the health and comfort of baby rabbits. Food should be neither too hot nor too cold. Food that is too hot can scald their delicate mouths and digestive systems, while food that is too cold can cause digestive issues. Similarly, water that is too cold can shock them.
Maintaining a safe temperature for both food and water ensures that they consume food comfortably and promotes proper digestion.
Sterilizing Equipment
Sterilization of feeding equipment is essential for preventing the transmission of diseases. Boiling equipment in water for a specific time is a reliable method of sterilization. This ensures that any potential harmful bacteria or pathogens are eliminated. Specific sterilization times depend on the type of equipment, and it’s crucial to consult reputable resources or veterinary guidelines for the precise sterilization times needed for each item.
Storing Food for Baby Rabbits
Proper storage of food is critical to maintain its quality and prevent spoilage. Store food in airtight containers in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. This prevents contamination and preserves the nutritional value of the food. Ensure the containers are labeled with the date of preparation and the type of food to avoid confusion.
Preparing Food for Consumption
The preparation steps should ensure that the food is in a suitable form for baby rabbits to consume. This includes ensuring that the food is at the correct temperature and that it’s finely chopped or shredded to prevent choking hazards. Carefully observe the baby rabbits’ reaction to the food and adjust the preparation accordingly.
Appropriate Temperatures for Different Food Types
| Food Type | Recommended Temperature (Celsius) |
|---|---|
| Fresh Vegetables (e.g., carrots, lettuce) | Room temperature (around 20-25°C) |
| Commercial Rabbit Pellets | Room temperature (around 20-25°C) |
| Fresh Fruits (e.g., berries, melon) | Room temperature (around 20-25°C) |
| Baby Rabbit Milk Replacer | Room temperature (around 20-25°C) |
| Fresh Herbs | Room temperature (around 20-25°C) |
Feeding Techniques and Schedules

Proper feeding techniques are crucial for the survival and healthy development of newborn rabbits. Consistent and appropriate feeding ensures the young rabbits receive the necessary nutrients for growth and prevents potential health issues. A well-structured feeding schedule, tailored to the specific needs of the newborns, is essential for their overall well-being.Feeding baby rabbits requires patience and attention to detail.
Understanding the various methods and adhering to a consistent schedule will contribute to the rabbits’ healthy development. Careful observation of the rabbits’ behavior during feeding is vital for assessing their well-being and adjusting the feeding approach as needed.
Methods of Feeding Baby Rabbits
Different methods are available for feeding baby rabbits, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Careful consideration of these factors will aid in selecting the most suitable method for the individual situation.
- Bottle Feeding: This method involves using a specialized bottle with a soft nipple to deliver milk or formula directly into the baby rabbit’s mouth. Advantages include precise control over the amount of food consumed and the ability to ensure hydration. Disadvantages include the need for consistent monitoring and potential for overfeeding or underfeeding if not meticulously managed.
Proper bottle feeding techniques are essential to prevent choking or discomfort for the rabbit.
- Dropper Feeding: Using a calibrated dropper allows for controlled amounts of milk or formula to be administered. This method is useful for newborns that may have difficulty latching onto a bottle. Disadvantages include potential for the rabbit to not ingest enough liquid and the increased time commitment for feeding. Consistency and accuracy in administering the liquid are essential for the baby rabbit’s survival.
Using a Feeding Bottle or Dropper
Correctly using a feeding bottle or dropper is paramount to successful feeding. These tools are critical for providing necessary nourishment to the baby rabbits.
- Bottle Feeding: Hold the bottle at a slight angle, ensuring the nipple is immersed in the milk or formula. Position the bottle near the baby rabbit’s mouth, allowing it to suckle naturally. Avoid forceful feeding, which can cause discomfort or choking. Always check the amount ingested to ensure proper intake and prevent overfeeding.
- Dropper Feeding: Hold the dropper at a slightly upward angle and gently place the tip near the baby rabbit’s mouth. Apply gentle pressure to release the liquid slowly and allow the baby rabbit to take it in. Ensure the baby rabbit doesn’t aspirate the liquid and maintain a steady, slow release.
Ensuring Proper Hydration
Adequate hydration is essential for newborn rabbits’ health. Maintaining proper hydration levels is crucial for their survival and growth.
- Frequent Feedings: Young rabbits require frequent feedings to maintain hydration and receive essential nutrients. A consistent feeding schedule is essential.
- Proper Formula: Use a specialized formula designed for baby rabbits, ensuring it contains all necessary nutrients, including electrolytes. Always consult a veterinarian for recommendations on formula.
Feeding Schedule for the First Few Weeks
A well-structured feeding schedule is critical for ensuring the proper nourishment of newborn rabbits. Consistency in the schedule promotes healthy growth and development.
| Week | Frequency | Amount per Feeding |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Every 2-3 hours | Small amounts, approximately 0.5-1 ml |
| 2 | Every 3-4 hours | Increased amounts, approximately 1-2 ml |
| 3 | Every 4-5 hours | Further increased amounts, approximately 2-3 ml |
| 4 onwards | Gradually increase feeding intervals | Transition to solid food |
Signs of Proper Feeding
Observing the baby rabbits’ behavior during and after feeding provides valuable insight into their well-being. Monitoring these signs allows for timely intervention if needed.
- Regular Feedings: The rabbits should show eagerness to feed and consume the formula.
- Steady Weight Gain: Regular weighing and monitoring of weight gain is essential.
- Normal Activity Levels: The rabbits should exhibit normal activity levels and not appear lethargic or stressed.
- Healthy Stool: Healthy stools indicate proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
Recognizing and Addressing Potential Issues

Monitoring baby rabbits’ health is crucial for their survival and well-being. Early detection of potential problems can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Careful observation and prompt intervention are essential to address any issues that arise during the feeding process.Identifying and resolving feeding problems promptly is vital for the healthy development of baby rabbits. Neglecting these issues can lead to serious health complications, hindering their growth and potentially causing irreversible damage.
Recognizing the symptoms of various problems allows for timely intervention and appropriate treatment.
Potential Feeding Problems in Baby Rabbits
Baby rabbits are highly susceptible to various feeding-related issues. Factors such as improper feeding techniques, inadequate nutrition, or underlying health conditions can contribute to these problems. Recognizing the signs of these problems is key to providing appropriate care.
Symptoms of Dehydration and Malnutrition
Dehydration and malnutrition are serious threats to baby rabbits. Dehydration manifests as sunken eyes, dry skin, and lethargy. Malnutrition, on the other hand, presents as stunted growth, weakness, and a lack of energy. Early detection of these symptoms is crucial for effective treatment. Rapid intervention is often necessary to prevent further complications.
Signs of Digestive Issues
Digestive problems in baby rabbits can range from mild discomfort to severe illness. Symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain. The consistency and color of the stool can provide valuable clues about the nature of the digestive problem. Prompt veterinary consultation is essential if digestive issues persist.
Actions for a Baby Rabbit Not Thriving
If a baby rabbit isn’t thriving, several actions can be taken. Firstly, review feeding practices to ensure appropriate amounts and types of food are being provided. Next, monitor the baby rabbit for any signs of illness or distress, such as dehydration, malnutrition, or digestive issues. Immediate veterinary attention should be sought if the rabbit’s condition worsens. The veterinarian can provide a diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate course of action.
Administering Medications (if necessary)
Medications may be necessary in certain situations. Always follow the veterinarian’s instructions carefully when administering medications to baby rabbits. Dosage should be precise and administered correctly to avoid potential side effects. Monitoring the rabbit’s response to the medication is essential.
Table of Potential Problems, Symptoms, and Solutions
| Potential Problem | Symptoms | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | Sunken eyes, dry skin, lethargy, reduced urination | Increase water intake, offer oral rehydration solutions (consult veterinarian), monitor closely |
| Malnutrition | Stunted growth, weakness, lack of energy, poor coat condition | Adjust feeding schedule and quantities, provide high-quality nutrition, consult veterinarian |
| Digestive Issues (Diarrhea, Vomiting) | Loose or watery stools, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal discomfort | Consult veterinarian, adjust diet, offer bland foods, monitor closely |
| Other Health Issues | Lethargy, loss of appetite, unusual behavior, abnormal discharge | Consult veterinarian immediately for diagnosis and treatment |
Supplementing the Diet for Optimal Growth

Ensuring baby rabbits receive a balanced diet is crucial for their healthy development. Beyond the essential food sources, supplementary vitamins and minerals play a vital role in supporting their growth and overall well-being. Careful attention to these additions, alongside a proper introduction of new foods, can significantly impact their growth trajectory.Adequate nutrition, encompassing both primary food sources and supplements, is paramount for fostering robust immune systems and promoting optimal skeletal and muscular development in young rabbits.
This careful approach to supplementing their diet ensures a positive impact on their future health and longevity.
Importance of Supplementary Vitamins and Minerals
Baby rabbits require a diverse range of vitamins and minerals for healthy growth. These nutrients support various bodily functions, including bone development, immune function, and energy production. A deficiency in even one essential nutrient can hinder their development, leading to potential health issues. Supplementation is crucial to bridge any gaps in their diet, ensuring a comprehensive intake of vital nutrients.
How to Incorporate Appropriate Supplements
Supplementation should be implemented with caution and under the guidance of a veterinarian. The appropriate type and dosage of supplements should be determined based on the specific needs of the baby rabbits. Consult a veterinarian to identify the necessary supplements and the recommended daily dosages. Improper supplementation can be detrimental to their health. Always follow veterinary recommendations.
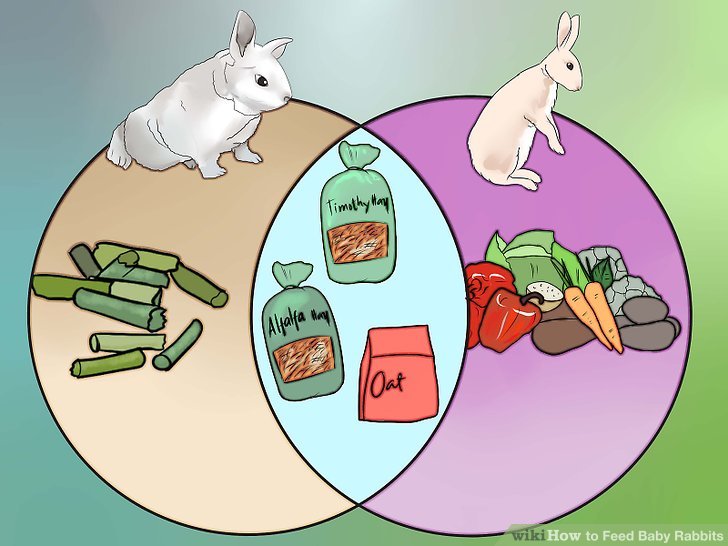
Importance of Providing Fresh Greens and Vegetables
Fresh greens and vegetables are invaluable additions to a baby rabbit’s diet, contributing significantly to their overall nutritional intake. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, promoting healthy digestion and supporting the development of a strong digestive system. Incorporating these fresh foods helps maintain a balanced diet.
Safe Vegetables and Greens for Baby Rabbits
A varied diet is crucial for a baby rabbit’s well-being. Introducing a range of safe vegetables and greens helps ensure they receive a broad spectrum of nutrients. A gradual introduction to new foods is vital to avoid digestive upset.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, romaine lettuce, dandelion greens (in moderation). These provide vital nutrients and fiber.
- Other Vegetables: Carrots (in moderation), sweet potato (in moderation), bell peppers (in moderation). These offer varied nutrients and flavors.
- Fruits: Small amounts of berries (strawberries, raspberries) are fine, but limit due to sugar content.
- Herbs: Parsley, cilantro (in moderation). These can be a delightful addition to their diet.
Gradual Introduction to New Foods
Introducing new foods gradually is essential. Start with small portions and observe for any signs of digestive distress, such as diarrhea or bloating. If no issues arise, gradually increase the portion size. This gradual approach helps prevent digestive upset and allows the baby rabbit’s system to adjust to the new food.
Safe Vegetables and Greens for Baby Rabbits: Portion Size Table
| Vegetable/Green | Portion Size (per day, estimate) |
|---|---|
| Romaine Lettuce | 1-2 small leaves |
| Carrot (peeled and chopped) | 1 small piece (1-2 cm) |
| Spinach | 1-2 small handfuls |
| Bell Pepper (chopped) | 1 small piece |
| Dandelion Greens | 1-2 small leaves |
| Sweet Potato (boiled and mashed) | 1 small piece (1-2 cm) |
| Berries (strawberries, raspberries) | 1-2 small pieces |
| Parsley | 1-2 small sprigs |
Note: Portion sizes are estimates and may need adjustment based on the baby rabbit’s size and individual needs. Always monitor for any digestive issues.
Preventing Common Feeding Errors
Proper feeding is crucial for the health and well-being of baby rabbits. Mistakes in feeding practices can lead to serious health problems, impacting their growth and development. Understanding common errors, their consequences, and preventative measures will help ensure your baby rabbits thrive.
Common Feeding Mistakes
Incorrect feeding practices can hinder a baby rabbit’s development and lead to various health complications. Understanding these mistakes is vital to provide optimal care.
- Overfeeding:
- Overfeeding can lead to obesity, digestive upset, and an increased risk of other health issues. Excess food can also result in nutrient imbalances and prevent the rabbit from absorbing essential vitamins and minerals properly. A baby rabbit should be fed only the amount they can consume without overeating.
- Underfeeding:
- Insufficient food intake will hinder the rabbit’s growth and development. They may experience nutrient deficiencies, leading to weakened immune systems and increased vulnerability to diseases. A consistent feeding schedule and appropriate portion sizes are critical for healthy growth.
- Inappropriate Food Choices:
- Offering unsuitable foods can be detrimental to a baby rabbit’s health. Some foods are toxic or indigestible for young rabbits. Strict adherence to a diet of appropriate foods is crucial for their proper development.
- Inadequate Water Supply:
- Dehydration can have severe consequences for baby rabbits, impacting their overall health and well-being. Always ensure a constant supply of fresh, clean water is available. This is especially important during times of high activity or temperature changes.
- Irregular Feeding Schedules:
- Inconsistency in feeding times can disrupt the baby rabbit’s digestive system, leading to discomfort and potential digestive problems. A regular schedule will help establish a healthy feeding pattern for optimal growth and development.
Consequences of Feeding Errors
The consequences of improper feeding practices can range from mild discomfort to serious health issues.
- Gastrointestinal Problems:
- Overfeeding or inappropriate food choices can cause digestive upset, diarrhea, or constipation in baby rabbits. These issues can lead to dehydration and further complications if not addressed promptly.
- Nutritional Deficiencies:
- Underfeeding or an unbalanced diet can result in a lack of essential nutrients, impacting growth, development, and overall health. This can manifest in weakened immune systems and an increased susceptibility to illness.
- Obesity:
- Excessive food intake can lead to obesity in baby rabbits, increasing the risk of health issues like heart problems, joint pain, and diabetes.
- Growth Retardation:
- Insufficient food intake or inappropriate food choices will significantly affect the growth rate of baby rabbits, leading to stunted development and overall weakened health.
Preventative Measures
Implementing preventative measures is essential to avoid common feeding errors.
- Precise Portion Control:
- Carefully measure the amount of food provided to baby rabbits, ensuring they consume only what they can eat in a short period without overeating.
- Strict Dietary Adherence:
- Stick to a diet specifically designed for baby rabbits, avoiding potentially harmful or indigestible foods.
- Consistent Feeding Schedule:
- Establish a regular feeding schedule to regulate their digestive system and ensure consistent nutrient intake.
- Fresh Water Availability:
- Ensure a constant supply of fresh, clean water in easily accessible containers.
Consulting a Veterinarian
It is crucial to consult a veterinarian if you have concerns about your baby rabbit’s health or feeding practices.
- Veterinary Guidance:
- A veterinarian can provide tailored advice based on your baby rabbit’s specific needs and condition. They can also diagnose any underlying health issues and recommend appropriate treatment.
Signs of an Unwell Baby Rabbit
Recognizing signs of illness is vital for timely intervention.
- Appetite Changes:
- A sudden loss or increase in appetite can be a sign of illness or discomfort. Monitoring eating habits is important for identifying potential problems.
- Lethargy or Weakness:
- Reduced activity levels, sluggishness, or weakness can indicate a range of health issues, requiring prompt veterinary attention.
- Changes in Stool Consistency:
- Significant changes in stool consistency (e.g., diarrhea, constipation) can be indicative of digestive problems or other health concerns.
- Abnormal Breathing:
- Difficulty breathing or unusual respiratory patterns warrant immediate veterinary attention.
- Unusual Discharge or Swelling:
- Any unusual discharge from the eyes, nose, or any swelling should be reported to a veterinarian immediately.
Summary of Common Errors
| Error | Consequences | Prevention Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Overfeeding | Obesity, digestive upset, nutrient imbalances | Precise portion control, monitoring consumption |
| Underfeeding | Growth retardation, nutritional deficiencies | Consistent feeding schedule, appropriate portion sizes |
| Inappropriate Food Choices | Digestive problems, toxicity | Strict adherence to appropriate rabbit food |
| Inadequate Water Supply | Dehydration, health complications | Constant fresh water availability |
| Irregular Feeding Schedules | Digestive disruptions, discomfort | Consistent feeding schedule |
Visual Guide to Feeding Baby Rabbits
Proper feeding techniques are crucial for the healthy development of baby rabbits. A visual guide will provide a clear understanding of essential aspects, from positioning to recognizing signs of distress. This comprehensive approach will ensure optimal nutrition and minimize potential issues.A visual representation of feeding techniques allows for clear understanding and application. The following sections detail the key elements of successful baby rabbit feeding, from positioning and administering food to recognizing signs of discomfort and utilizing appropriate equipment.
Positioning the Baby Rabbit
Correct positioning during feeding is vital for the rabbit’s comfort and to ensure proper food intake. A supportive surface, like a soft cloth or towel, is essential to prevent the baby rabbit from slipping or feeling stressed. The rabbit should be held gently but firmly, supporting its body and preventing any undue pressure on its chest or belly. The rabbit should be held with the head facing upwards and slightly angled toward the food source, ensuring the baby rabbit’s mouth is readily accessible for feeding.
This approach reduces stress and improves the feeding experience for the animal.
Feeding Techniques
Various feeding techniques can be used depending on the situation. A crucial aspect of feeding baby rabbits is using a very small amount of food, and gradually increasing the quantity and variety as the rabbit matures. The feeding process should be gentle and controlled, avoiding any forceful pushing of food into the rabbit’s mouth. A gentle, spoon-like motion with a small amount of food, and then a pause to allow the rabbit to eat, is preferable.
Amount of Food
The amount of food offered to a baby rabbit must be meticulously monitored. Start with very small quantities, approximately the size of a few small grains of food, to avoid overfeeding. Gradually increase the amount as the rabbit demonstrates increased appetite and the ability to consume larger quantities. Overfeeding can lead to digestive issues, while underfeeding will impede growth and development.
Observing the rabbit’s eating habits and adjusting portions accordingly is crucial for healthy growth.
Signs of Discomfort or Distress
Recognizing signs of discomfort or distress during feeding is critical. If the rabbit appears restless, squirming, or showing signs of difficulty swallowing, reduce or stop the feeding immediately. Monitor the rabbit’s breathing rate and overall body posture for any changes that may indicate discomfort. Signs like rapid breathing, excessive crying, or limpness may signal distress. Any of these indicators necessitate immediate attention and veterinary consultation.
Feeding Equipment
Proper feeding equipment is essential for maintaining hygiene and ensuring the rabbit’s well-being. Using small, clean feeding utensils, like tiny spoons or medicine droppers, prevents contamination and ensures precise food administration. These utensils should be sterilized and kept clean between feedings. Always use sterilized water for the baby rabbits. Use a clean, soft towel or cloth to gently support the rabbit during feeding to minimize stress and promote comfort.
Feeding Scenarios
The following table illustrates various feeding scenarios, emphasizing proper technique:
| Scenario | Positioning | Food Amount | Technique | Signs of Distress |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeding a newborn | Support the body gently, head slightly elevated. | Pinhead-sized amount of food. | Spoon-like motion, pause for eating. | Restlessness, difficulty breathing, squirming. |
| Feeding a growing rabbit | Hold firmly but gently, allowing access to food. | Small pea-sized amount of food. | Use a small spoon, gently guide food to the mouth. | Difficulty swallowing, refusing food, limpness. |
| Feeding a weaned rabbit | Allow free access to food. | Small quantities of solid food. | Offer food in a shallow dish. | Refusal to eat, weight loss, diarrhea. |
Final Summary
In conclusion, successfully feeding baby rabbits requires careful attention to detail and a deep understanding of their specific needs. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the entire process, from initial feeding to recognizing and addressing potential problems. By following the Artikeld feeding schedules, hygiene practices, and supplemental care strategies, you can ensure the healthy growth and development of your baby rabbits.
Remember, a healthy diet and proper care are essential for their well-being.